这是发表在 ICML 2018 上的一篇关于 MIL 的文章,文章内容其实挺简单,但是讲的很好,其中MIL的思想可以借鉴。
文章的开源代码在 AttentionDeepMIL 。
MIL将许多instances看作一个bag,然后对这个bag赋予一个label。
在这篇文章中,作者将MIL问题看作是学习bag标签的Bernoulli分布(二项分布),通过优化对数似然函数来训练模型,提出了一个
neural network-based permutation-invariant aggregation operator that corresponds to the attention mechanism
。
MIL处理的问题是:现在有许多instances,把它们看作一个bag,但是只给了一个bag的标签。MIL的主要目标就是学习一个模型来预测bag的标签,另外,还希望能够发现key instances (the instances that trigger the bag label),这样能提高模型的可解释性。
对bag probability的建模分为3步:
- a transformation of instances to a low-dimensional embedding;
- a permutation-invariant(symmetric) aggregation function;
- a transformation to the bag probability.
其中所有的参数都是由神经网络训练得到的(只有卷积层和全连接层)。
Multiple Instance Learning
对于a bag of instances: \(X = \{ x_1, \dots, x_K \}\),其中的instances既没有依赖关系,也没有顺序,对于不同的bag可以有不同的K值(数量)。其中每个instance都有未知标签\(y_k \in \{ 0, 1\}, k=1,\dots, K\),假设bag的标签这么定义:(这个公式的排版有点捉急了...)
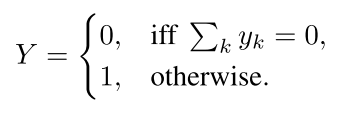
其实这就说明了MIL模型是permutation-invariant(排列无关/与顺序无关)的了,公式(1)也等价于
\[
Y = \mathop{\max}\limits_{k} \{y_k\} \tag{2}
\] 通过优化log-likelihood
function来训练MIL模型,bag标签的分布服从Bernoulli分布,参数\(\theta(X) \in [0, 1]\),即给定bag \(X\)时\(Y=1\)的概率。
MIL问题可以看做Fundamental Theorem of Symmetric Functions的一个特例。
Theorem 1.
A scoring function for a set of instances \(X\), \(S(X) \in R\), is a symmetric function (i.e., permutation- invariant to the elements in \(X\)), if and only if it can be decomposed in the following form: \[ S(X) = g(\sum_{x \in X}f(x)) \tag{3}, \] where \(f\) and \(g\) are suitable transformations.
Theorem 2.
For any \(\epsilon > 0\), a Hausdorff continuous symmetric function \(S(X) \in R\) can be arbitrarily approximated by a function in the form \(g(\max_{x \in X}f(x))\), where max is the element-wise vector maximum operator and \(f\) and \(g\) are continuous functions, that is: \[ | S(X) - g(\max_{x \in X}f(x)) | < \epsilon ,\tag{4} \]
这两个定理对于bag的分类任务给出了一般的求解步骤:
- a transformation of instances using the function \(f\)
- a conbination of transformed instances using a symmetric function \(\sigma\)
- a transformation of combined instances transformed by \(f\) using a function \(g\)
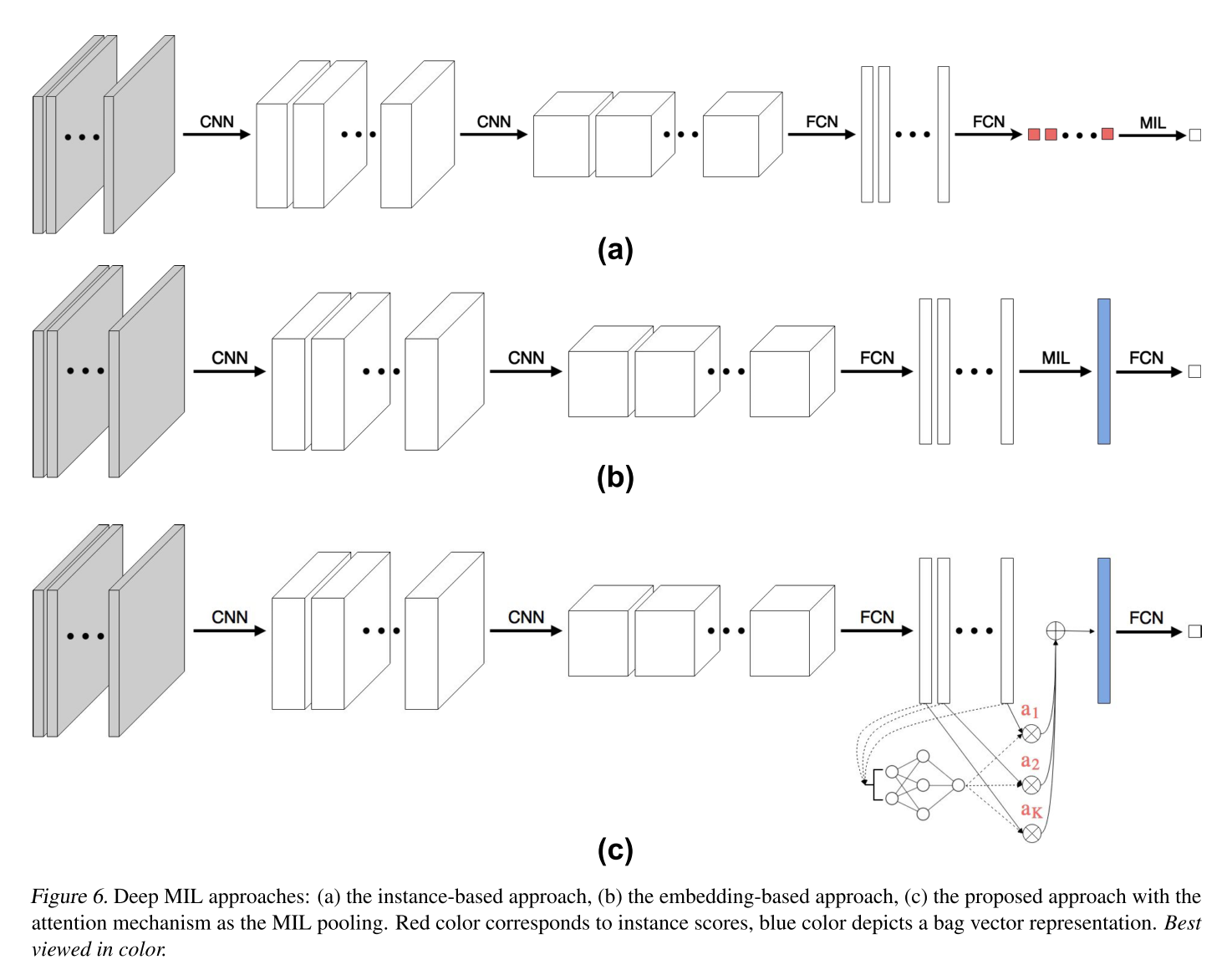
应用起来就是: (1) CNN 提取特征; (2) pooling (max pooling | avg pooling | MIL pooling); (3) FC层。
The embedding-level approach: The function \(f\) maps instances to a low-dimensional embedding. MIL pooling is used to obtain a bag representation that is independent of the number of instances in the bag. The bag representation is further processed by a bag-level classifier to provide \(\theta(X)\).
Attention-based MIL pooling
使用max-operator有两点不足:pre-defined and non-trainable。希望使用attention mechanism来增加模型的灵活性和可解释性。
公式也不复杂,就是各个instances在low-embedding后的softmax加权平均,和之前的MIL pooling的对比如下图所示:
最后实验部分,作者给出了这个方法在MNIST数据集和一个组织病理学数据集上的实验,证明其有效性。